FRP Grating (Fiber Reinforced Plastic Grating) is a strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant material widely used in industrial and commercial projects. Many companies prefer it over steel, aluminum, or wood because it lasts longer, is safer, and requires less maintenance.
This guide gives you a complete overview of FRP Grating. You will learn what it is, its main types, how it is manufactured, where it can be used, how to maintain it, and how it compares to other materials. It also explains standards, costs, and future trends. Whether you are new to FRP or an experienced professional, this article is a practical reference.
What Is FRP Grating?
FRP Grating is a grid-like structure made of fiberglass reinforcement and thermosetting resin. It is designed to provide strength, durability, and safety in environments where traditional materials might fail.
Composition: fiberglass + polyester, vinyl ester, or epoxy resin
Core Properties: lightweight, strong, corrosion-resistant, slip-resistant, non-conductive
👉 Related Reading: FRP vs GRP Grating: Key Differences and How to Choose
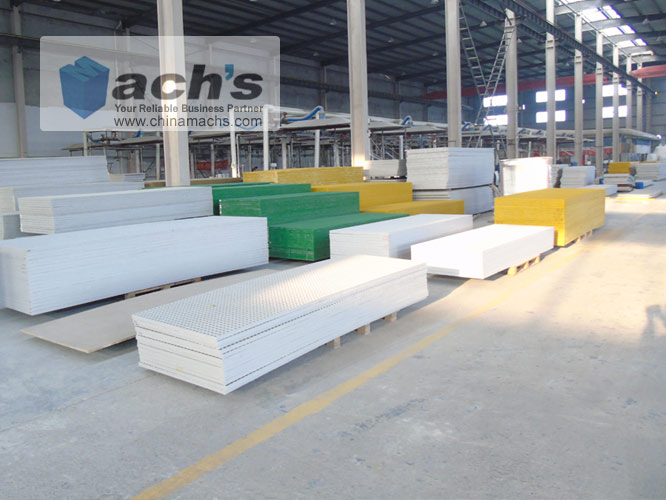

Main Types of FRP Grating
Different types of FRP Grating are suitable for different applications:
Molded Grating: made in one piece by casting fiberglass and resin in a mold. Excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for chemical plants and wet areas.
Pultruded Grating: made from pultruded profiles assembled into a grid. High mechanical strength, suitable for heavy loads and long spans.
Customized Grating: designed for specific needs, such as fire resistance, special surface textures, or unique colors.
Manufacturing Processes
FRP Grating is manufactured through two main processes:
Molded Process: fiberglass mats are layered in a mold, resin is poured, and the product is cured into a solid piece. Provides consistent corrosion resistance.
Pultrusion Process: continuous fiberglass strands are pulled through resin and a heated die, forming profiles that are later assembled into gratings. Stronger in mechanical load-bearing.
Molded gratings are preferred in highly corrosive environments, while pultruded gratings are chosen for structural strength.
Machs on-site production of FRP Grating video
Structures and Surface Options
FRP Grating comes in different structures depending on its function:
Open Mesh: good drainage and ventilation, often used in walkways and platforms.
Covered Grating: solid top surface to prevent spillage, dripping, or falling objects.
Slip-Resistant Surface: gritted or serrated finish for safety in wet or oily environments.
Dimensions and Specifications
FRP Grating is available in a range of sizes and load ratings.
Thickness: common options are 25 mm, 38 mm, and 50 mm
Mesh Size: 38×38 mm and 40×40 mm are typical
Load Range: from pedestrian traffic to light vehicle loads, depending on type and thickness
👉 Related Reading: Common FRP Grating Sizes and Applications
Performance and Testing
FRP Grating’s reputation comes from its reliable performance, which is verified by international testing standards.
Mechanical Properties: bending strength and impact resistance
Corrosion Resistance: tested against acids, alkalis, and salts
Slip Resistance: measured on gritted or serrated surfaces
Weathering Resistance: UV and color stability under outdoor use
Fire Resistance: resin formulations tested under ASTM or ISO standards
👉 Related Reading: The Complete Guide to FRP Grating Performance Tests
Applications of FRP Grating
The versatility of FRP Grating makes it useful across many industries:
Chemical & Petrochemical Plants: safe walkways and operating platforms in corrosive zones
Water & Wastewater Treatment: drainage covers, clarifier walkways, and sludge tank platforms
Power & Energy: non-conductive working platforms and cooling tower structures
Transportation: pedestrian bridges, subway entrances, and public walkways
Marine & Offshore: ship decks, docks, and coastal facilities where saltwater exposure is high
FRP Grating’s durability reduces downtime and ensures safety in all these areas.
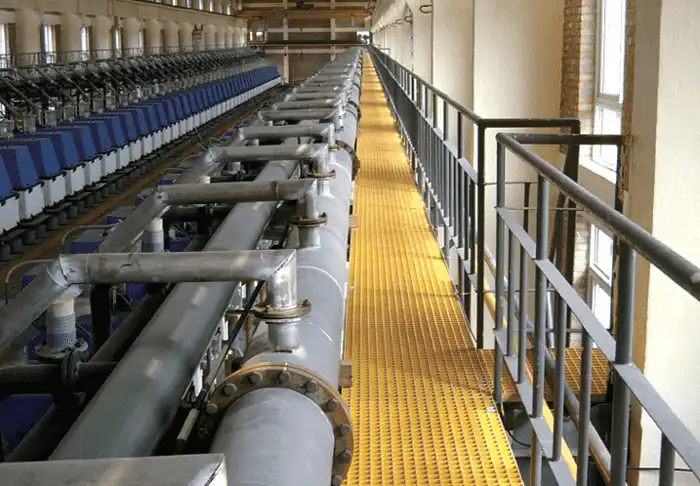

Installation and Fixing
Proper installation ensures that FRP grating stays safe and stable in use. Panels are usually fixed to steel or concrete structures with clips and fasteners to prevent movement.
Space should be left for thermal expansion and contraction, especially outdoors. This avoids warping and stress over time.
When cutting panels, care must be taken not to damage the fiberglass reinforcement. Any broken fibers may reduce strength and durability.
Regular checks after installation are important to make sure clips remain tight and the structure stays secure.
👉 Related Reading: Grating Clips for FRP Grating: Types, Functions, and Installation Best Practices
Maintenance and Cleaning
Even though FRP Grating is low-maintenance, regular care helps extend its lifespan.
Use high-pressure water or mild detergent to remove dirt and debris
Inspect regularly for cracks, surface wear, or exposed fibers
Reapply anti-slip coatings when needed
Replace damaged panels immediately to maintain safety
👉 Related Reading: FRP Grating Maintenance and Cleaning: How to Extend Service Life and Reduce Costs
FRP Grating vs Other Materials
Many buyers compare FRP with traditional materials before deciding.
Steel Grating: cheaper upfront but heavy, prone to rust, requires frequent painting or galvanizing
Aluminum Grating: lightweight, good strength, but limited corrosion resistance and not insulating
Wood or Concrete: low cost, but short service life, prone to rot, cracks, and high maintenance
Overall, FRP Grating provides the best balance between durability, safety, and cost efficiency.
Standards and Certifications
FRP Grating is tested and certified under global standards:
ASTM D635 – flame spread
ASTM E84 – surface burning characteristics
ISO 14122 – safety for industrial walkways and platforms
EN 13706 – pultruded profile standard
These certifications ensure safety and quality for industrial use.
Cost and Economic Value
FRP Grating may have a higher initial price compared to steel or wood, but its life-cycle cost is lower.
No need for repainting or anti-corrosion treatments
Longer lifespan (20–25+ years)
Reduced maintenance labor and downtime
High return on investment in corrosive environments
👉 Related Reading: FRP Grating Cost and Economic Value: What You Need to Know
How to Choose the Right FRP Grating
Selecting the right FRP Grating depends on project needs:
Application Environment: chemical plants need corrosion resistance; ports need slip resistance
Load Requirements: pedestrian traffic vs vehicle loading
Budget Planning: consider life-cycle cost, not only upfront investment
Manufacturer Reliability: certifications, production capacity, and proven project cases
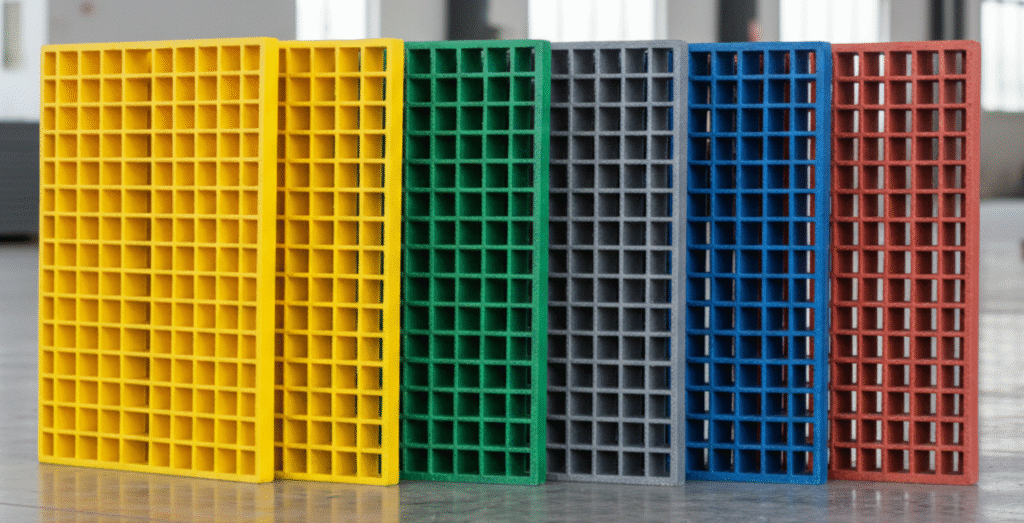
Colors and Visual Options
FRP grating comes in different colors to suit both safety and design needs. Gray is the most common choice for general industrial use.
Green is often selected for environmental or water treatment projects, while yellow is widely used in safety zones to mark hazardous areas. The use of color helps workers and operators quickly identify spaces and reduce risks.
For outdoor projects, UV-resistant pigments can be added. This prevents fading and ensures the grating keeps its appearance even after long exposure to sunlight.
Future Trends in FRP Grating
The FRP Grating industry is evolving with technology and sustainability:
Development of eco-friendly resins with lower emissions
Improved fire-retardant and UV-resistant properties
Smart manufacturing for customized designs and faster delivery
Wider adoption in renewable energy projects and infrastructure
FAQ: Common Questions About FRP Grating
How long does FRP Grating last?
Typically 20–25 years or more, depending on environment.
Is FRP Grating conductive?
No, it is electrically insulating, making it safe for power facilities.
Can FRP Grating resist fire?
Yes, with fire-retardant resin systems meeting ASTM and ISO standards.
Can it handle vehicle loads?
Pultruded heavy-duty types can support light vehicles and forklifts.
Conclusion
FRP Grating is a versatile, durable, and safe solution for industries ranging from chemical plants to marine facilities. It combines strength, corrosion resistance, low maintenance, and long-term cost savings.
This guide provides a full framework for understanding FRP Grating—from its definition, types, and performance to installation, maintenance, and future prospects. For deeper insights, check the related articles linked throughout this page.
If you are considering FRP Grating for your project, working with a certified and experienced manufacturer will ensure you get the right product at the best value.


