FRP handrails are now widely used in industry and public facilities. They are made from fiberglass reinforced plastic, a material valued for strength, safety, and resistance to harsh environments. Unlike steel or wood, FRP needs little maintenance and lasts much longer. This makes it a cost-efficient and reliable choice.
This guide gives you a clear overview of FRP handrails. It covers what they are, their key benefits, common types, standards, applications, and how to choose the right system. Whether you are an engineer, a contractor, or a buyer, this article will help you make better decisions.
What Are FRP Handrails?
FRP handrails are structural railing systems made from fiberglass reinforcements and thermosetting resin. They are designed to provide safety and support in walkways, platforms, stairs, and industrial structures.
The material composition gives FRP handrails unique properties. They are lightweight but strong, non-conductive, and resistant to corrosion. This makes them especially suitable for environments where traditional metal or wooden handrails fail.
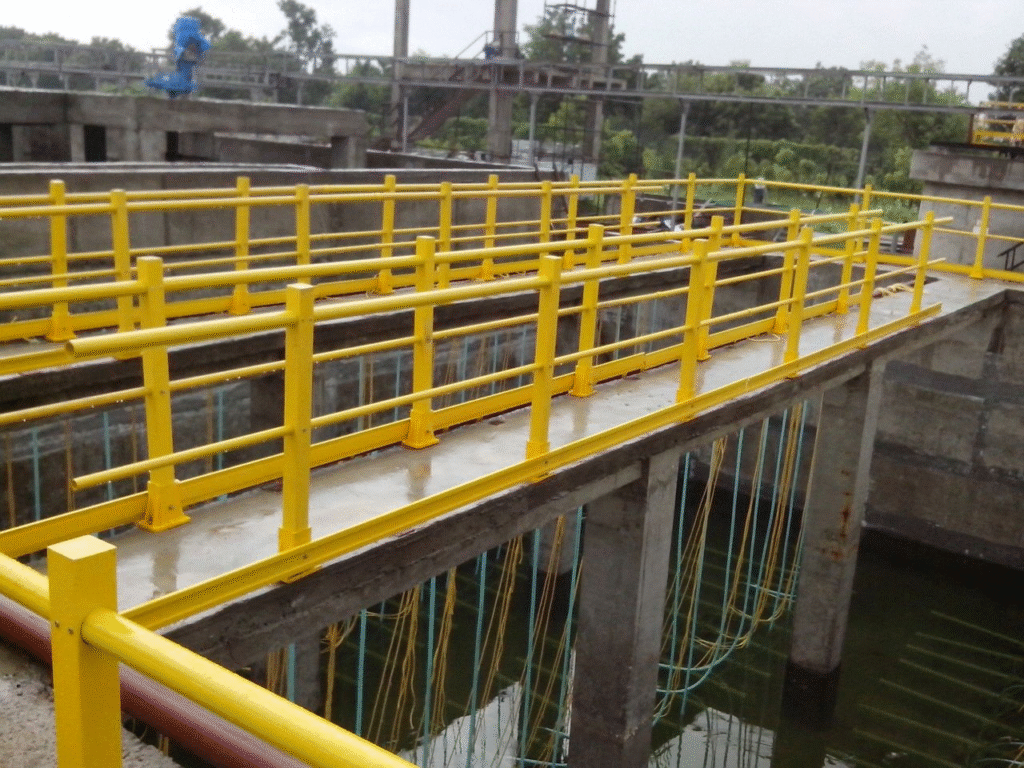

Key Benefits of FRP Handrails
Corrosion Resistance
One of the strongest advantages of FRP handrails is their ability to resist corrosion. In chemical plants, wastewater facilities, or marine docks, steel handrails are prone to rust. FRP, however, maintains performance even under constant exposure to moisture, chemicals, or salt.
Lightweight and Strong
FRP handrails weigh less than steel or aluminum systems. This reduces transportation and installation costs while maintaining sufficient strength to meet safety standards. The strength-to-weight ratio of FRP is one of the main reasons it is used in industrial environments.
Electrical Insulation
Unlike metal, FRP does not conduct electricity. This makes FRP handrails ideal for electrical facilities, power stations, and any environment where safety against electrical hazards is critical.
Low Maintenance
FRP handrails do not require painting, galvanizing, or regular surface treatment. They are easy to clean with water or mild detergent, lowering maintenance costs over the life of the system.
Long Service Life
The average lifespan of FRP handrails ranges between 20 and 25 years. In some controlled environments, it can last even longer.
Common Types of FRP Handrails
Standard Industrial Handrails
These are the most common FRP handrail systems used in factories, warehouses, and plants. They are designed to provide safe boundaries on platforms and walkways.
Safety Handrails
Often used together with slip-resistant flooring or grating, safety handrails protect workers in hazardous areas. Bright colors, such as yellow, are frequently used to increase visibility.
Custom Handrails
Projects with unique requirements may need handrails with different heights, angles, or finishes. FRP systems can be customized to match project specifications.
Modular Systems
Some FRP handrail systems are designed as modular kits. Pre-fabricated posts, rails, and connectors allow quick installation without welding.
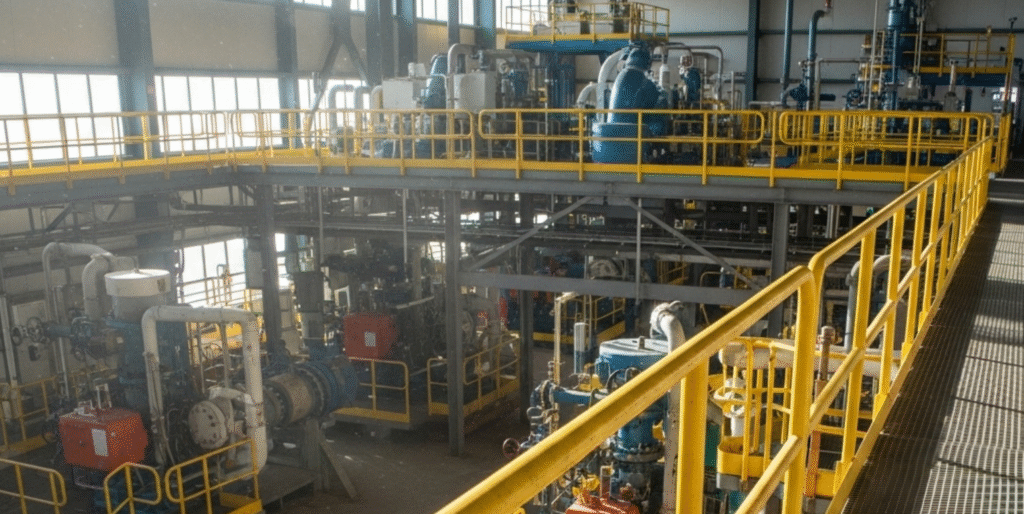
Design Standards and Compliance
International Standards
FRP handrails must comply with industrial safety codes. In the United States, OSHA standards regulate the minimum height of railings and the loads they must withstand. ASTM and ISO standards also cover fire performance, strength, and quality control.
Safety Parameters
Handrail height is typically around 42 inches (1067 mm). The system must resist horizontal loads without failure. For stairs, intermediate rails and toe boards may be required to prevent accidents.
Applications of FRP Handrails
Industrial Plants
In factories and processing plants, FRP handrails are used along walkways, staircases, and platforms. Their resistance to chemicals makes them a safe and reliable choice.
Marine and Offshore
Ships, docks, and offshore platforms need railings that can withstand saltwater exposure. FRP does not rust or corrode in these environments, making it the preferred option.
Water and Wastewater Treatment
Facilities dealing with sewage or treated water require corrosion-resistant materials. FRP handrails are installed around tanks, clarifiers, and treatment platforms to protect workers.
Public Infrastructure
In public spaces such as bridges, overpasses, and stairways, FRP handrails provide both safety and low maintenance. Their bright colors and clean finish also add to the visual appeal.
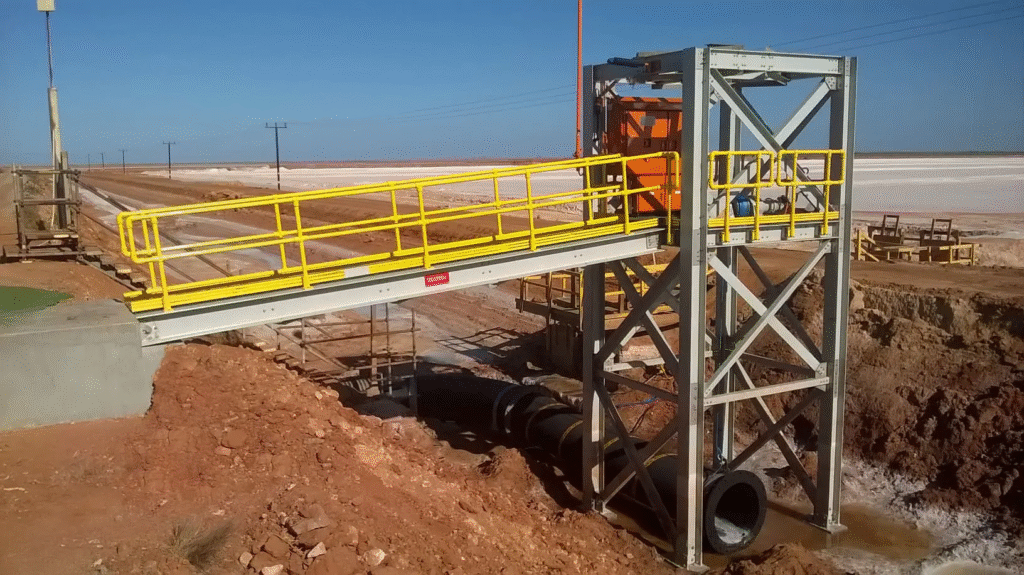

Installation and Fixing
Modular Installation
FRP handrails are often supplied in modular parts, making installation straightforward. Rails, posts, and connectors are joined with bolts or clamps, reducing the need for specialized labor.
Site Adjustments
Panels can be cut to size on-site, but care must be taken not to damage the fiberglass reinforcement. Precision cutting ensures the system keeps its structural strength.
Regular Checks
Once installed, the system should be inspected periodically. Tightening bolts and checking connectors help prevent accidents and extend the service life of the handrail system.
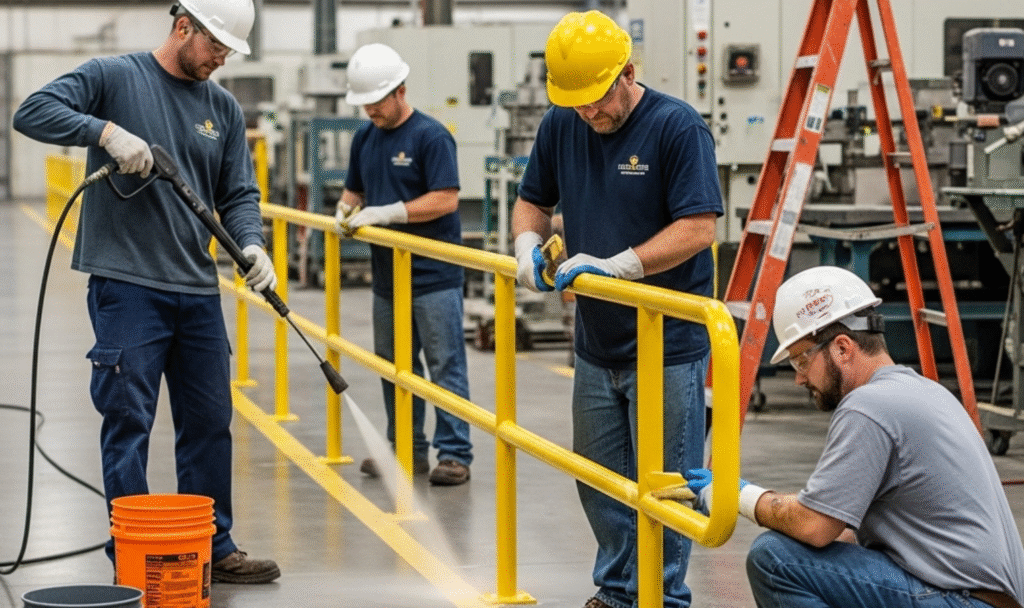
Maintenance and Service Life
Easy Cleaning
FRP handrails can be cleaned using water or mild cleaning agents. This is often enough to remove dirt, chemicals, or salt.
Inspection Points
Owners should look for surface cracks, loose fasteners, or fading colors. Small issues can be corrected before they affect safety.
Expected Lifespan
Owners should look for surface cracks, loose fasteners, or fading colors. Small issues can be corrected before they affect safety.

FRP Handrails vs Other Materials
FRP vs Steel
Steel is strong but heavy and prone to rust. It requires painting or galvanizing and regular inspections. FRP, while lighter, resists corrosion and offers similar strength for most applications.
FRP vs Aluminum
Aluminum is lightweight and easier to install than steel. However, it still conducts electricity and offers less corrosion resistance compared to FRP.
FRP vs Wood
Wood handrails are cheap but not durable in industrial or outdoor environments. They are prone to rot, insects, and structural weakness over time.
Cost and ROI of FRP Handrails
The upfront cost of FRP handrails may be slightly higher than steel or wood, but the total life-cycle cost is lower. The savings come from:
Reduced maintenance
No painting or galvanizing
Longer service life
Less downtime for replacement
When evaluating return on investment, FRP handrails often prove more economical over 20 years than metal systems.
How to Choose the Right FRP Handrail System
Step 1: Define the Environment
Identify if the project involves exposure to chemicals, saltwater, or electricity.
Step 2: Determine Load Requirements
Understand whether the system will be used by pedestrians, in heavy industrial plants, or near machinery.
Step 3: Review Standards
Check which safety codes apply, including OSHA, ASTM, or ISO requirements.
Step 4: Select Type and Configuration
Choose between standard, modular, or custom designs depending on the project.
Step 5: Work with Reliable Manufacturers
Ensure the supplier provides certifications, project references, and consistent quality.
Future Trends in FRP Handrails
Sustainable Materials
Manufacturers are developing eco-friendly resins and recyclable composites to meet sustainability goals.
Improved Fire and UV Resistance
Advances in resin formulations are making FRP handrails more resistant to fire and long-term outdoor exposure.
Wider Adoption
FRP handrails are expanding beyond industrial use, with growing demand in public infrastructure and commercial projects.
Conclusion
FRP handrails combine durability, safety, and cost efficiency in one solution. They resist corrosion, require little maintenance, and provide reliable performance across industries. By understanding their benefits, applications, and standards, you can choose the right system for your project.
With proper installation and maintenance, FRP handrails can serve for decades, protecting people and reducing costs at the same time.


