FRP grating, also known as Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic grating, is a high-performance material used in chemical plants, marine platforms, wastewater facilities, and power stations. It is light, strong, and highly resistant to corrosion.
But how do we know it is safe and reliable? The answer lies in performance testing. Every panel goes through a series of tests before it reaches the customer. These tests check strength, durability, slip safety, fire behavior, and resistance to harsh environments.
This guide explains how FRP grating is tested and why these tests matter.
1. Visual and Dimensional Inspection
The first step in any quality process is appearance and size checking.
Surface inspection: Look for cracks, bubbles, or surface defects.
Dimensions: Confirm panel length, width, thickness, and mesh size meet design tolerance.
Flatness: Ensure the panel lies evenly to avoid problems during installation.
Only panels that pass this step move forward to performance testing.
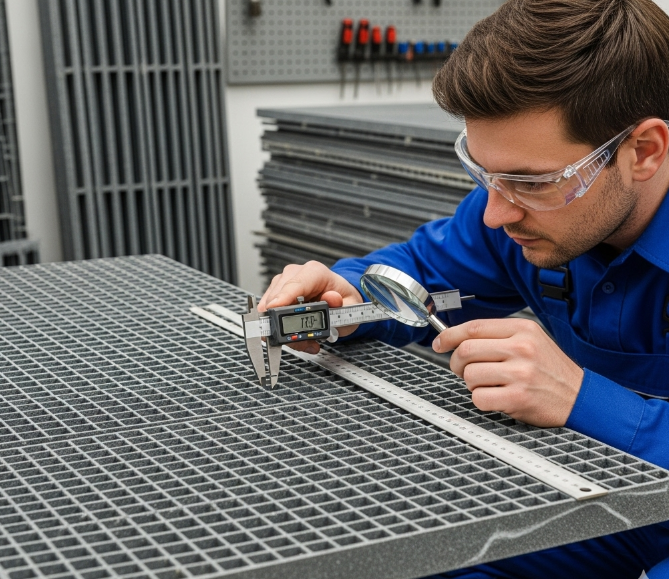

2. Mechanical Performance Tests
Flexural (Bending) Strength
Factories use bending tests such as ASTM D790 or ISO 14125 to measure how much load the grating can handle before it bends or breaks. This is critical for safe use in platforms and walkways.
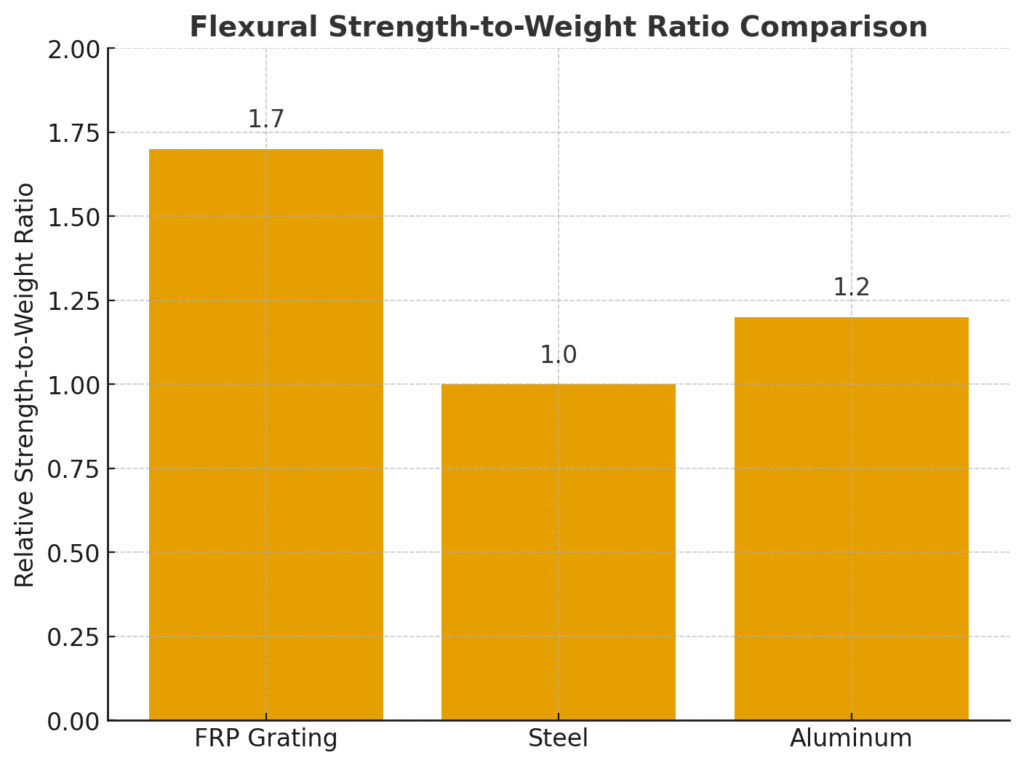
FRP grating shows about 1.7x strength-to-weight advantage over steel, and higher than aluminum as well:
FRP Grating = 1.7
Steel = 1.0 (baseline)
Aluminum = 1.2
👉 This advantage means FRP grating can support heavy loads while remaining lightweight.
Tensile and Compressive Strength
Tensile test (ASTM D638): Measures how much pulling force the material can resist.
Compressive test (ASTM D695): Measures resistance under crushing loads.
These tests confirm FRP’s structural reliability under both pulling and pressing forces.
Impact Resistance
Factories run impact tests like Izod or Charpy (ASTM D256). A weight strikes a sample to test toughness.
Why it matters: Confirms that FRP grating will not fail suddenly if struck by tools or falling objects.
Hardness and Abrasion Resistance
Hardness is checked using the Barcol hardness test (ASTM D2583).
Why it matters: Ensures the surface can withstand traffic, scratches, and wear in industrial settings.

3. Environmental Durability Tests
Chemical Resistance
Samples are soaked in acids, alkalis, and salts following ASTM D543. Factories measure how much strength the panel retains.
Example: FRP retains >95% strength after 30 days in common chemicals.
👉 This makes it ideal for chemical plants and wastewater treatment.
UV and Weathering Resistance
Panels are exposed to UV, heat, and moisture using accelerated aging tests (ASTM G154).
Ensures FRP can survive outdoor exposure without losing strength or color.
Water Absorption
Measured with ASTM D570. Low absorption ensures resin bonds remain strong.
4. Slip Resistance and Walking Safety
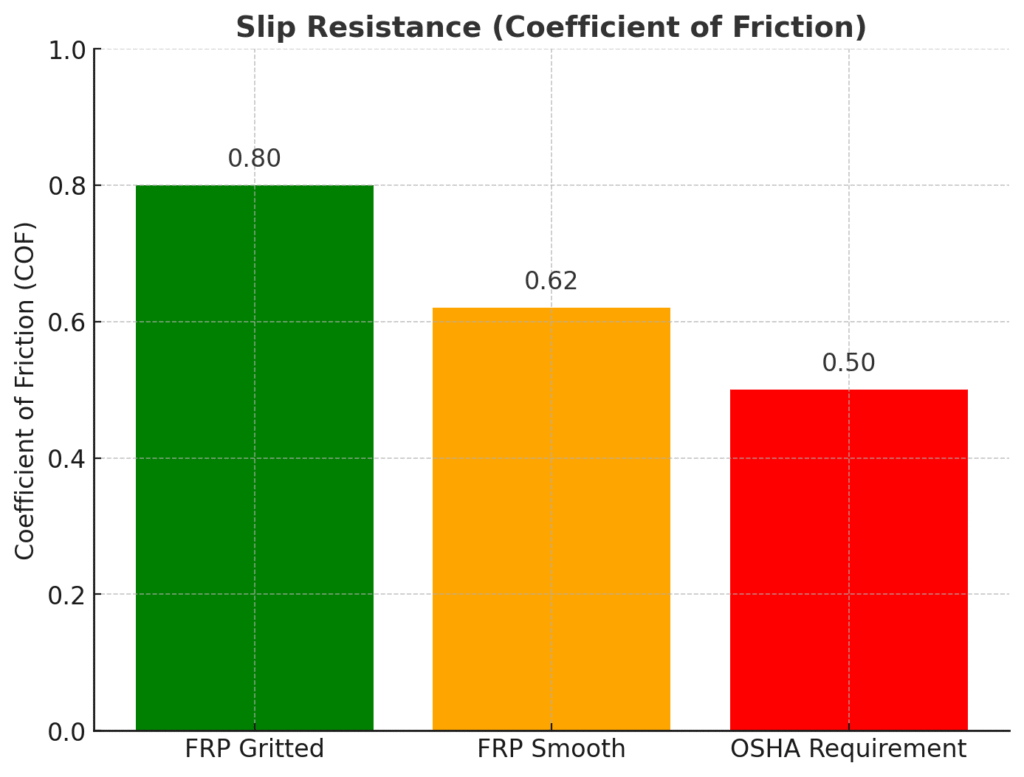
Slip resistance is measured using the Coefficient of Friction (COF). Standards like ASTM D2047 apply.
📊 Example:
FRP gritted surface: COF = 0.80
FRP smooth surface: COF = 0.62
OSHA requirement: ≥ 0.50
👉 FRP with a gritted surface provides excellent safety in wet or oily areas.
5. Fire and Safety Testing
FRP gratings are tested under fire safety standards:
ASTM E84: Flame spread index and smoke development.
UL94: Flammability of plastic materials.
ASTM D635: Burning rate.
Example: Vinyl ester FRP gratings often achieve a flame spread index <25, which meets many building codes.
6. Panel-Level Load and Fatigue Testing
Beyond small sample tests, full grating panels are tested under real conditions:
Load-deflection tests: Panels are loaded until they reach maximum deflection limits.
Fatigue tests: Panels undergo repeated loading cycles to simulate years of use.
👉 This proves that entire panels—not just samples—are safe for long-term service.
7. Additional Performance Factors
Factories may also check:
Thermal expansion: FRP expands less than plastics but more than steel; important in large installations.
Antistatic properties: Useful in explosive environments.
Color stability: For projects requiring long-lasting appearance.
8. Compliance and Certification
High-quality FRP gratings are backed by certification and standards, such as:
ASTM F3059: Marine specification for FRP gratings.
ISO 9001 quality management systems.
Industry guidelines from ACMA.
Buyers should always ask for:
Test reports from accredited labs.
Span tables showing safe loads.
Certificates proving compliance with fire and slip resistance standards.
Conclusion
FRP grating is trusted in demanding industries because it is strong, durable, and resistant to harsh conditions. These qualities are not assumptions—they are proven through performance tests.
From visual checks and bending strength tests to chemical resistance, slip safety, fire ratings, and fatigue tests, each step ensures FRP gratings perform reliably. For engineers, project managers, and buyers, understanding these tests is the key to selecting safe and high-quality products.
👉 In short: tested FRP grating means long-lasting safety and performance.


